Build an Automated Document Workflow for High-Quality RAG Retrieval
Unlock superior AI accuracy by building a smarter automated document workflow. Learn RAG-optimized chunking, metadata, and architecture strategies that work.
An automated document workflow is the engine that turns messy, raw files—like PDFs and Word documents—into clean, structured data that a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system can actually understand and use.
This process replaces slow, error-prone manual preparation with a repeatable, scalable pipeline. It’s the foundational step to guarantee your RAG system has high-quality, retrievable information to generate accurate answers.
The Foundation of High-Quality RAG Retrieval
For any RAG system built to answer questions from a knowledge base, the quality of its answers is directly tied to the quality of the data it can find. An automated document workflow isn't just about efficiency; it’s a non-negotiable requirement for building a reliable and accurate RAG system.
Without it, you're stuck with inconsistent data preparation that leads directly to poor retrieval, irrelevant context being passed to the LLM, and a frustrating user experience.
Imagine trying to build a modern search engine by having librarians manually read, summarize, and tag every single book in a massive library. The process would be slow, subjective, and riddled with errors. Automation fixes this by creating a predictable, machine-driven pipeline that treats every document with the exact same set of rules, making your knowledge base reliable and consistent.
From Raw Files to RAG-Ready Data
An effective workflow systematically moves documents through critical stages designed to refine raw information, making it optimized for retrieval by an AI model. This structured approach is what separates a high-performing RAG system from one that constantly returns irrelevant answers.
The key stages in this process look something like this:
- Ingestion: The starting point, where documents in various formats (PDF, DOCX, Markdown, etc.) are gathered and loaded into the system.
- Preprocessing: The cleanup phase. Raw text is scrubbed of junk characters, formatting issues are fixed, and content is prepared for analysis. This heavily involves data parsing.
- Chunking: The document is strategically broken down into smaller, meaningful pieces, or "chunks." These are the units of information your RAG system will retrieve.
- Enrichment: Valuable context—like source page, section titles, or extracted keywords—is added as metadata to each chunk. This gives the retrieval system vital clues for finding the right information.
- Indexing: The prepared chunks and their metadata are converted into numerical representations (embeddings) and stored in a specialized vector database built for fast, semantic retrieval.
Why Automation is No Longer Optional
The old method—manual processing—is completely unsustainable at scale. Manual work creates inconsistencies, makes it impossible to track changes, and becomes a massive bottleneck that stops you from quickly improving your RAG system's performance.
As more organizations rely on AI to extract value from their documents, the need for robust automation has become urgent.
An automated workflow ensures that every piece of information entering your AI's knowledge base is processed consistently, tagged accurately, and structured for optimal retrieval. It's the assembly line that turns raw materials into precision parts for your AI engine.
To see just how big this shift is, look at the market for intelligent document processing (IDP). It's projected to explode from $10.6 billion in 2025 to over $66 billion by 2032. This trend makes it clear that automated document handling is shifting from a nice-to-have tool to essential business infrastructure, especially for AI. Mastering this process is how you build a real competitive advantage.
Manual vs Automated Document Workflow for RAG
The difference between a manual approach and a modern automated workflow is night and day. One is a bottleneck; the other is an accelerator for RAG performance.
| Stage | Manual Workflow (The Old Way) | Automated Workflow (The RAG-Ready Way) |
|---|---|---|
| Ingestion | Manually uploading and sorting files one by one. Slow and prone to errors. | Automatically ingests files from multiple sources (S3, GDrive, API). |
| Parsing | Copy-pasting text, often losing formatting, tables, and structure. | Intelligently extracts text, tables, and images while preserving layout. |
| Chunking | Arbitrarily splitting text, creating inconsistent and out-of-context chunks. | Uses semantic or structural rules for coherent, context-aware chunks. |
| Metadata | Inconsistent or non-existent tagging, relying on human memory. | Automatically extracts and attaches rich metadata (source, page, headings). |
| Scalability | Doesn't scale. Adding more documents requires more people and time. | Scales effortlessly to handle thousands or millions of documents. |
| Consistency | Highly variable results depending on who is doing the work. | 100% consistent and repeatable, ensuring uniform data quality. |
| Iteration | Extremely slow to update or re-process the knowledge base. | Re-process the entire knowledge base in minutes or hours, not weeks. |
Ultimately, a well-designed automated workflow isn't just about saving time. It's about creating a reliable, high-quality foundation that allows your RAG system to perform at its best.
Architecting a High-Performance RAG Pipeline
A high-performance RAG system is only as good as its foundation. And that foundation is a well-designed automated document workflow, built from the ground up for one thing: optimal retrieval. Think of it like designing a library’s entire cataloging system before the first book ever hits a shelf.
Every decision you make in this pipeline directly impacts how well your Large Language Model (LLM) can find and use information. A weak link anywhere in this chain, whether it's sloppy text cleaning or a slow database, will tank the accuracy and speed of your final output. It’s the classic principle: garbage in, garbage out.
This diagram lays out the core stages of the pipeline, from when a document first enters the system to when it’s fully indexed and ready for queries.
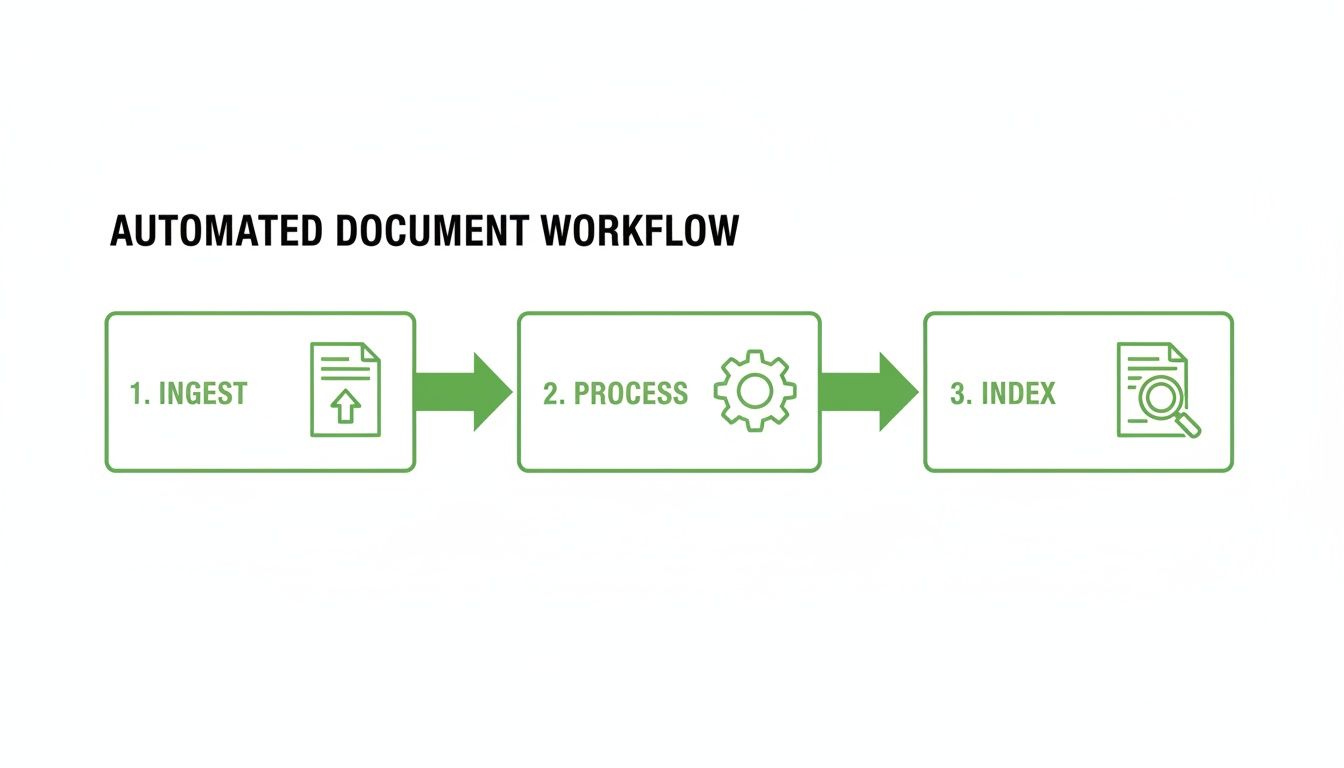
As you can see, a solid RAG pipeline is a linear process. Each step methodically prepares the documents for the next, all leading to a searchable, high-quality knowledge base. Let’s break down what really happens at each stage.
Ingestion and Preprocessing
It all starts with ingestion. This is where you pull in documents from all your different sources. Your system needs to be ready to handle a mess of formats—PDFs, DOCX files, Markdown, you name it—without mangling the important structural information. Simply ripping out raw text isn’t good enough; a robust parser should understand layouts, tables, and headers to preserve context.
Right after that comes preprocessing, the cleanup crew. This is your first chance to combat low-quality data. It involves stripping out junk characters, extra whitespace, and irrelevant page headers or footers. If you don't get this right, your LLM ends up trying to make sense of corrupted information, which leads straight to inaccurate retrieval results.
Chunking and Metadata Enrichment
With clean text in hand, the next step is chunking. This is where you strategically split the document into smaller, semantically coherent pieces. The goal is to create chunks that are small enough for an LLM to process efficiently but large enough to contain useful, self-contained context. A poor chunking strategy, like cutting a paragraph in half, can destroy meaning and make retrieval impossible.
Immediately after chunking, you move on to metadata enrichment. This is where you wrap each chunk in layers of valuable context.
Metadata is what turns a simple blob of text into a smart, queryable object. It’s the difference between asking a librarian for "a book that mentions finance" versus asking for "all books by Jane Doe on European stock markets published in 2023."
To enable powerful retrieval, you should add key metadata, including:
- Source Information: The original filename, page number, and document author.
- Structural Context: Which section heading or title the chunk belongs to.
- Summaries: A concise summary of the chunk's content for fast relevance checks.
- Keywords: Any extracted entities like names, dates, or product codes.
This structured data is absolutely essential for enabling more powerful hybrid search techniques down the line.
Vectorization and Indexing
The final steps prepare the data for search. In the vectorization stage, an embedding model converts each text chunk into a numerical vector. This vector is a mathematical representation of the chunk's semantic meaning, allowing a machine to understand conceptual relationships between different pieces of text.
Finally, during indexing, these vectors and their attached metadata are loaded into a specialized vector database. Your choice of database is critical. It directly affects query speed, scalability, and your ability to run complex filtered searches. A well-built index allows the RAG system to sift through millions of documents in milliseconds to find the precise snippets of information needed to answer a user's question.
Mastering Document Chunking for Precise Retrieval
 Document chunking is the absolute heart of RAG retrieval accuracy. It’s the process of thoughtfully splitting large documents into smaller, contextually rich pieces.
Document chunking is the absolute heart of RAG retrieval accuracy. It’s the process of thoughtfully splitting large documents into smaller, contextually rich pieces.
Think of it like preparing study notes for your AI. Tearing pages out of a textbook at random creates a confusing mess. But carefully creating flashcards based on individual concepts makes the information clear and easy to recall. That's what good chunking does.
The goal isn't just to make smaller text blobs; it's to preserve the original meaning within each chunk. A sloppy chunking strategy can sever critical links between sentences, leading your RAG system to pull up useless, out-of-context fragments. A well-designed automated document workflow uses intelligent chunking to give the AI the best possible context—the secret to precise, accurate answers.
Comparing Practical Chunking Strategies
Different documents demand different game plans. You can't treat a dense legal contract the same way you'd handle a structured technical manual. Choosing the right chunking strategy is a make-or-break decision that directly shapes retrieval quality.
Here are actionable strategies, from basic to sophisticated:
- Fixed-Size Chunking: The brute-force method of splitting a document every 500 characters. Actionable Insight: Avoid this strategy. While simple, it almost always cuts sentences mid-thought, destroying context and leading to poor retrieval performance.
- Paragraph Splitting: A significant improvement. This strategy splits the document along natural paragraph breaks. Actionable Insight: Use this as a solid baseline for general documents. It's effective because paragraphs usually contain a complete thought, but be aware of its limitations with very long paragraphs or unconventional formatting.
- Heading-Based Chunking: For structured documents like manuals or reports, this method is a game-changer. It uses the document's hierarchy to create chunks that map to specific sections. Actionable Insight: This is the preferred method for any document with a clear
H1/H2/H3structure, as it naturally preserves the author's intended context.
The choice you make is foundational to your RAG system's success. For a deeper look, you can explore more advanced chunking strategies for RAG systems to see how different approaches stack up.
The Power of Semantic Chunking
Semantic chunking is an advanced method that moves beyond simple rules. It uses AI models to understand the text and identify natural topic breaks, grouping sentences based on their conceptual similarity.
Imagine a complex technical manual where one section discusses both "Installation" and "Troubleshooting" without a clear subheading. A semantic chunker can intelligently separate these distinct topics into different chunks.
Actionable Insight: Use semantic chunking when your documents contain dense, mixed-topic paragraphs. When a user asks about an installation problem, the RAG system retrieves only the relevant installation steps, not unrelated troubleshooting advice. It's a massive improvement for retrieval relevance.
Semantic chunking is like having an expert editor who reads your documents and intelligently divides them into logical, self-contained topics. This gives your AI the cleanest possible data to work with, dramatically improving the relevance of its search results.
Visualizing and Validating Your Chunks
The best strategy on paper doesn't always work perfectly in the real world. That’s why visual validation is so critical. You need to see exactly how your chosen chunking strategy is splitting your documents and where things might be going sideways.
Actionable Insight: Use tools like ChunkForge that provide a visual overlay mapping every chunk back to its source pages. This immediate feedback loop lets you spot awkward splits, confirm context is preserved, and trace every piece of information. By visually testing and tweaking your approach, you can be confident that your automated document workflow is producing logical, high-quality chunks that will empower your RAG system to find information with precision.
Using Metadata to Supercharge RAG Accuracy
Relying on semantic search alone is like asking a librarian to find a specific fact in a massive library with no card catalog. They might eventually find it by browsing conceptually similar books, but it’s slow and often imprecise.
Metadata is that card catalog. It's the secret weapon for moving your RAG system from decent to exceptionally accurate. By adding structured metadata to your chunks, you unlock the power of pre-filtering—a crucial step where you dramatically narrow the search space before the vector search even begins. This hybrid approach is faster, more efficient, and delivers far more relevant results.
The Power of Hybrid Search
Imagine you need to find "revenue figures in Q4 from the European division" buried within thousands of financial reports. A pure vector search might pull up chunks that smell right because they mention "revenue" or "Europe," but it could easily miss the specific Q4 detail or pull in numbers from the wrong region.
Now, let's try a hybrid search powered by metadata.
The system first applies a precise filter to find all chunks tagged with {'quarter': 'Q4', 'region': 'Europe'}. Instead of searching the entire database, it now performs a vector search on a tiny, highly relevant subset of data. The odds of retrieving the exact information you need just went way up.
This two-step "filter-then-search" process is the core of any high-performance RAG system. It combines the precise, rule-based logic of metadata filtering with the nuanced, meaning-based power of semantic search.
An effective automated document workflow doesn't just create chunks; it enriches them with layers of this invaluable context.
Essential Metadata for Precision Retrieval
Not all metadata is created equal. To build a robust retrieval system, your workflow should focus on automatically extracting and attaching several key types of structured data to every single chunk.
Here are the most impactful metadata types for improving retrieval:
- Structural Tags: Foundational context like the original filename, page number, and section/chapter titles. This helps users trace information back to its source, building trust in your AI.
- Entity Extraction: Automatically identify and tag key entities—people, organizations, locations, dates, product names, and monetary values. When a query mentions a specific company, the system can filter for chunks explicitly tagged with that company.
- Chunk Summaries: A concise, one-sentence summary of each chunk can be stored as metadata. This allows the system to perform a quick relevance check during the filtering stage without processing the full chunk text.
Automating the extraction of this data is fundamental for building a scalable and reliable knowledge base.
From Text to Structured Insight
One of the most powerful enrichment techniques is Named Entity Recognition (NER). NER models scan text to automatically identify and categorize key information, turning unstructured sentences into structured, queryable data.
This is what allows a system to understand that "Acme Corp" is an organization and "Q2 2024" is a date. If you want to see how it works under the hood, you can learn more about named entity recognition in NLP.
Enforcing Consistency with JSON Schemas
The final piece of the metadata puzzle is consistency. You can't have a reliable system if it's messy.
If one part of your workflow tags a date as "quarter": "Q4" and another uses "period": "Fourth Quarter", your filtering logic will break. This is where custom JSON schemas become your best friend.
Actionable Insight: Define a strict schema to enforce a consistent structure and data type for all your metadata. For example, you can require that every chunk has a source_filename (string), a page_number (integer), and a publish_date (date format). This data discipline ensures your metadata is reliable and ready to supercharge retrieval accuracy across your entire knowledge base.
Implementing a Resilient and Scalable Workflow
<iframe width="100%" style="aspect-ratio: 16 / 9;" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/TRjq7t2Ms5I" frameborder="0" allow="autoplay; encrypted-media" allowfullscreen></iframe>Getting an automated document workflow running is one thing. Building one that’s resilient, scalable, and improves over time is another. The best workflows are living systems, not static setups. You’re not just processing documents; you’re constantly refining the quality of the information you extract to improve retrieval.
This begins with getting the fundamentals right. Rigorous data cleaning and normalization are non-negotiable. They prevent the classic “garbage in, garbage out” trap that dooms so many RAG systems. A workflow built on a clean foundation is more reliable and easier to manage.
Adopting Evaluation-Driven Development
To graduate from a decent workflow to a great one, embrace evaluation-driven development. This means treating your retrieval performance as the most important metric guiding your decisions.
Actionable Insight: Build a benchmark "golden set" of questions and their ideal answers. This represents the queries your RAG system must get right. Run these questions against your indexed data to get a hard number on your retrieval performance. When a query fails, trace the failure back to its root cause in your automated document workflow. Was the chunking strategy wrong? Was critical metadata missing? This feedback loop lets you pinpoint weaknesses and make targeted fixes to your chunking and enrichment rules, making the system smarter with every test.
The Human-in-the-Loop Advantage
Automation isn't about replacing people; it's about making them more effective. A human-in-the-loop (HITL) model is the perfect example. Let machines handle the high-volume, repetitive work, freeing up your experts to supervise tricky edge cases and exceptions.
The returns on this approach are clear. Recent data shows that 60% of organizations see a positive ROI within just 12 months of implementing workflow automation. Companies report productivity jumps of 25-30% and error reductions of 40-75%. With modern document processing tools hitting over 90% extraction accuracy, the HITL model becomes incredibly efficient. Get more stats on the tangible benefits of workflow automation.
By embracing a human-in-the-loop system, you transform automation from a replacement tool into a force multiplier. Your team's expertise is reserved for the most complex challenges, improving both efficiency and the overall quality of your knowledge base.
Build Versus Buy: The Modern Middle Ground
When implementing an automated document workflow, teams often face the "build vs. buy" dilemma. Building from scratch offers total control but requires a huge engineering lift. Buying a proprietary tool can be faster, but you often face data lock-in and limited customization.
Thankfully, there’s a powerful middle ground: open-source, self-hostable tools. A solution like ChunkForge exemplifies this approach. It provides a production-ready, highly configurable environment for the hardest parts of the pipeline—ingestion, chunking, and metadata enrichment—while being completely open-source.
This model gives you the best of both worlds: the speed of a specialized tool without sacrificing control over your data or infrastructure. By using such a component, your team can stop reinventing the wheel and focus on building the unique parts of your application, letting you create a scalable workflow much faster.
Frequently Asked Questions
Building a solid automated document workflow for RAG always surfaces a few practical questions. Here are some direct answers to the most common challenges we see developers and engineers run into.
How Do I Choose the Right Chunking Strategy for My Documents?
There's no magic bullet—the best chunking strategy is dictated by your document's structure and your retrieval goals. The key is to match the technique to the content.
For highly structured files like technical manuals, Heading-based chunking is usually your best bet because it respects the document's built-in hierarchy. For dense, unstructured text like a research paper, Semantic chunking often produces more coherent results by finding natural topic shifts. For most general document types, Paragraph splitting is a reliable starting point.
Actionable Insight: Start with the simplest method that gives you decent results (like paragraph splitting) and iterate. Always test a few strategies on a sample document and visually inspect the output to see which one creates the most logical chunks for your expected queries.
What Is the Difference Between Semantic Search and Metadata Filtering?
Think of them as two different tools that work together in a powerful hybrid search system.
Semantic search is about meaning. It finds data based on conceptual similarity, not just keyword matching. This helps understand what the user really wants.
Metadata filtering is a precise, rules-based process. It narrows the search space using structured tags like {'region': 'EMEA', 'year': 2023}. It's exact—a document either matches the filter or it doesn't.
Actionable Insight: The most effective RAG systems use both. They first apply metadata filters to instantly reduce the dataset to only the most relevant documents. Then, they run a semantic search within that smaller, pre-filtered set to pinpoint the best passage. This two-step process is much faster and more accurate than relying on semantic search alone.
Can I Build This Workflow Without Specialized Tools?
Absolutely. You can build an automated document workflow from the ground up with open-source libraries like LangChain, LlamaIndex, and various PDF parsing tools. This route gives you maximum control.
However, be prepared for the engineering lift. Building, debugging, and maintaining this kind of pipeline from scratch is significant work. You'll be writing custom code for different document types, implementing chunking algorithms, ensuring metadata consistency, and wiring it all to your vector database.
Specialized tools exist to short-circuit this process. They offer a production-ready, configurable environment for the trickiest parts—ingestion, chunking, and enrichment. This frees up your team to focus on core application logic. The choice depends on your team's resources, timeline, and where you want to focus your energy.
How Should I Handle Document Updates in My Knowledge Base?
Managing document updates is critical for preventing stale or conflicting information in your RAG system. The best practice is to design an idempotent pipeline, where re-processing the same document multiple times produces the exact same result.
Actionable Insight: Assign every document a unique, persistent identifier. When a new version of a document arrives, your workflow should first delete all existing chunks and metadata associated with that ID from your vector database. After clearing the old data, process the updated document through the entire pipeline as if it were new. This "delete-then-re-index" strategy ensures your knowledge base stays current and your RAG system always uses the latest information.
Ready to stop wrestling with document processing and start building a smarter RAG system? ChunkForge provides the visual tools and powerful chunking strategies you need to create a high-performance, automated document workflow. Get started with ChunkForge today—try it for free or self-host the open-source version to maintain full control over your data.