Actionable Guide to Automation Document Processing for R-Grade RAG
Discover automation document processing for smarter RAG results, practical tips on chunking, enrichment, and retrieval to unlock data insights.
Automation document processing is the critical first step in building a high-performing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system. It’s the engine that transforms your raw, unstructured files—like PDFs, reports, and messy text documents—into clean, structured, and discoverable assets ready for your AI. The primary goal is simple: prepare your data so that your retrieval system can find the exact context needed to generate accurate, trustworthy answers.
The biggest challenge isn't just processing documents; it's optimizing that process to supercharge retrieval. Poor retrieval leads to irrelevant context, which is the root cause of AI hallucinations and unreliable responses.
The Blueprint for High-Precision Retrieval
Staring at a mountain of unstructured documents can feel overwhelming. Buried inside those PDFs and Word files is priceless knowledge, but to a Large Language Model (LLM), it's all just noise in its raw form. Automation document processing provides an actionable blueprint for turning that noise into a high-signal knowledge base optimized for retrieval.
Think of it as preparing a dataset for a high-stakes investigation. You wouldn’t just dump raw files on an analyst's desk. You would organize, index, and annotate them so that any piece of evidence can be found in an instant. This process systematically breaks down, cleans, and enriches your documents, making them perfectly suited for a sophisticated RAG system.
Why This Process Is the Bedrock of RAG
For any Retrieval-Augmented Generation system, one rule is absolute: retrieval quality dictates generation quality. The context you retrieve is the only "world" the LLM knows when crafting its answer.
If your processing pipeline produces poorly structured or noisy chunks, your retrieval system will fetch irrelevant context. This irrelevant context is what causes LLMs to "hallucinate" or generate confidently incorrect answers. Nailing your document processing is the most impactful action you can take to build a reliable AI.
A retrieval-focused pipeline delivers concrete advantages:
- Sharper Retrieval Accuracy: Well-structured, clean data chunks enable your vector database to pinpoint the most semantically relevant context for any query.
- Reduced AI Hallucinations: Providing the LLM with precise, factual context from your documents anchors its responses in verifiable truth.
- Built-in Traceability: A robust processing pipeline makes it easy to trace an AI’s answer back to the exact source document, a non-negotiable for building trust and allowing for verification.
The core action is to shift your mindset: stop seeing your documents as a static archive and start treating them as a dynamic, queryable knowledge base designed to make your retrieval system succeed.
The Growing Need for Automation
The demand for intelligent processing is surging. The Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) market is projected to reach USD 91.02 billion by 2034, growing at an aggressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.20% from 2026.
This reflects an urgent need for businesses to automate how they extract value from documents, eliminating manual toil and the costly errors that come with it.
This guide provides an actionable blueprint for building a retrieval-first processing system. We'll cover the foundational stages and advanced strategies, showing you exactly how to transform raw documents into high-octane fuel for any RAG application. For a deep dive into the entire workflow, check out this complete guide to automatic document processing for business.
Building Your Automated Document Processing Pipeline
Think of your document processing workflow as a high-tech assembly line designed for one purpose: producing perfectly structured, retrieval-ready data for your RAG system. Each station has a specific job, taking a raw, messy file and progressively refining it into an intelligent asset. This pipeline isn't just about processing; it's about preparation for peak retrieval performance.
The journey starts with your raw documents and ends with AI-ready intelligence. Let's walk through each critical stage of this transformation.
The flowchart below shows the basic path from unstructured data to intelligent, actionable insights.
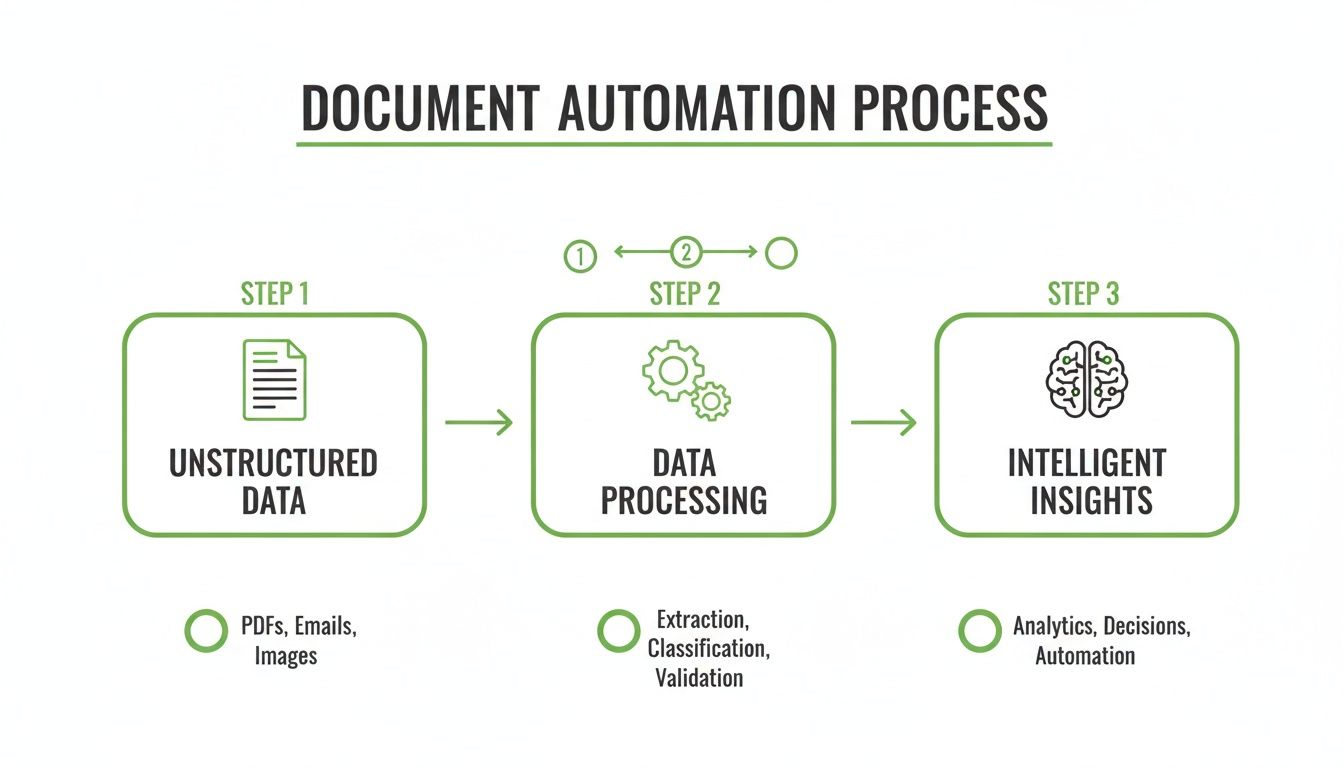
This visual simplifies the core concept: raw documents go into a processing engine where they're structured and cleaned, ultimately becoming useful assets the AI can draw upon.
The Six Core Stages Of The RAG Data Pipeline
To build a system that delivers accurate, context-aware answers, you must optimize each of these stages for retrieval. A failure at any point degrades the performance of your entire RAG application.
-
Ingest This is the entry point. Your ingest stage must reliably extract raw text and structural elements (like tables or headings) from diverse file types—PDFs, DOCX, Markdown, HTML, etc. The actionable insight here is to ensure your ingestion tool preserves as much structural information as possible, as this can be used later for more advanced chunking and metadata strategies.
-
Preprocessing Raw text is messy. This stage is your cleanup crew. It removes noise that degrades retrieval quality, such as irrelevant headers, footers, formatting artifacts, or OCR errors. Clean text leads to cleaner vector embeddings, which directly translates to more accurate similarity searches.
-
Chunking This is where strategy is paramount for retrieval. Instead of indexing a whole document, you break it into smaller, meaningful pieces called chunks. The goal is to create chunks that are semantically self-contained. A well-formed chunk provides a complete, coherent piece of information when retrieved, giving the LLM clear context to work with.
Good chunking is arguably the single most critical factor for RAG success. An actionable tip is to visualize your chunks against the source document to ensure you aren't splitting key ideas or tables, which would destroy their contextual value upon retrieval.
-
Enrichment Once you have chunks, you add metadata. This is a powerful tactic to improve retrieval beyond simple vector similarity. Enrichment involves adding structured data like summaries, keywords, or custom tags (e.g.,
department: "legal",status: "final"). This metadata enables hybrid search, allowing you to pre-filter chunks based on factual criteria before performing a vector search. -
Vectorization Here, you convert your clean, enriched text chunks into numerical representations called vector embeddings using an embedding model. These vectors capture the semantic meaning of the text. The key action is to use the same embedding model for both your documents and your user queries to ensure that semantic comparisons are accurate.
-
Retrieval This is where your preparation pays off. A user's query is also converted into a vector. Your system then performs a search in the vector database to find the text chunks with the most similar vectors. By combining this with metadata filtering, you can retrieve highly relevant nuggets of information that are then passed to the LLM to generate a factually grounded answer. This process ensures the AI's response is tethered to your data, not its generic training.
Mastering Document Chunking For Superior Retrieval
If preprocessing is about tidying up your text, chunking is where the real strategic work of automation document processing begins. This is the single most impactful step for determining whether your RAG system's retrieval will be precise or chaotic.
Get it right, and you retrieve sharp, relevant context. Get it wrong, and you feed the LLM noisy, confusing junk that leads to unreliable answers.
Chunking is the art and science of breaking large documents into smaller, semantically coherent pieces. Each chunk must be meaningful enough to stand alone yet small enough to be retrieved with pinpoint accuracy. Think of it as creating highly specific, context-rich index cards for your entire knowledge base.

Choosing Your Chunking Strategy
There is no one-size-fits-all chunking strategy. The optimal approach depends entirely on your document's structure and the types of questions you anticipate. The key is to choose a strategy that best preserves the context needed for accurate retrieval.
-
Fixed-Size Chunking: The simplest method. You slice the document into fixed-length chunks (e.g., 500 characters) with some overlap (e.g., 50 characters) to maintain context across boundaries. Actionable insight: Use this for unstructured text or as a quick baseline, but be aware it often cuts sentences and ideas in half, which can harm retrieval quality.
-
Paragraph-Based Chunking: A much more context-aware approach. This method splits documents along natural paragraph breaks. Since paragraphs typically contain a single coherent idea, this strategy excels at preserving semantic integrity. Actionable insight: Make this your default strategy for well-structured documents like articles, reports, and manuals.
-
Semantic Chunking: The most advanced technique. It uses an embedding model to group sentences based on their semantic similarity, identifying natural thematic breaks in the text. This ensures each chunk is a highly coherent package of related information. Actionable insight: Use this for dense, complex documents like legal contracts or academic papers where meaning is nuanced and spans across sentences.
A common pitfall is applying one chunking strategy across all document types. The actionable approach is to test different strategies on representative samples of your documents and evaluate the resulting chunks for coherence.
For a much deeper dive into these methods and more, check out our complete guide on choosing chunking strategies for RAG.
Choosing The Right Document Chunking Strategy
Selecting the right strategy is a trade-off between implementation simplicity and contextual preservation. This table provides actionable guidance on where each method excels.
| Strategy | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-Size | Quick prototypes and unstructured text with no clear formatting. | Extremely simple and fast to implement, requiring minimal text analysis. | Often breaks sentences and splits concepts, leading to fragmented context. |
| Paragraph | Well-structured documents like reports, articles, and user manuals. | Preserves the natural flow of ideas and is highly effective for narrative text. | Can create very large or very small chunks, depending on paragraph length. |
| Semantic | Dense, complex documents like legal contracts or research papers. | Creates highly coherent, contextually rich chunks based on meaning. | Computationally more expensive and slower than other methods. |
Ultimately, the most actionable advice is to experiment. Test different strategies on your documents and, most importantly, visually inspect the output. Ask yourself: does this chunk make sense on its own? If not, your retrieval system will struggle.
Visualizing And Verifying Your Chunks
Theory is one thing, but execution is another. A major challenge in building RAG pipelines is the inability to see how chunking logic is performing. You're often flying blind, hoping your strategy is creating clean splits instead of shredding valuable context.
This is where visual tools become an absolute game-changer for improving retrieval. A platform that lets you see each generated chunk mapped directly back to its source in the original document provides instant, actionable feedback.

For instance, a tool like ChunkForge provides a visual overlay that helps you immediately spot awkward splits or verify that a chunk contains all the context it needs. This direct mapping lets you see if a chunk ends abruptly or misses key information, so you can fine-tune your window size and overlap settings with confidence.
By visualizing the output, you replace guesswork with an iterative, data-informed process, dramatically accelerating development and leading to far more accurate retrieval.
Using Metadata Enrichment For Pinpoint Accuracy

While smart chunking lays the foundation, metadata is the force multiplier that elevates your RAG system's retrieval from good to exceptional. Relying solely on vector similarity means you are only searching in one dimension. Adding metadata creates layers of structured, filterable context that transforms a simple vector search into a high-precision retrieval engine.
This is the most direct way to give your users more control and improve relevance. Think of online shopping: you don't just search for "shirt." You apply filters for size, color, and brand. Metadata provides that same filtering power to your automation document processing pipeline, enabling far more accurate retrieval.
Moving Beyond Semantic Search Alone
Vector search excels at finding conceptually similar information but struggles when users need to find something based on specific, factual criteria.
For example, a query like "Project Alpha's budget from the Q4 2023 financial report" could be matched with any chunk mentioning "Project Alpha" or "budgets." This is where metadata enrichment becomes a powerful, actionable tool.
By attaching specific attributes to every chunk, you can implement a hybrid search strategy. The system first narrows the search space to only include chunks matching the specified metadata (e.g., document_type: "financial_report", quarter: "Q4", year: 2023) before performing the vector search.
Actionable insight: Metadata acts as a powerful pre-filter. It drastically reduces the search space, ensuring the vector search operates only on a highly relevant subset of data. This boosts retrieval accuracy and improves efficiency.
This hybrid approach ensures retrieved results are not just semantically similar but also factually correct according to the user's explicit criteria.
Powerful Metadata Enrichment Techniques
Enriching your chunks with quality metadata is a game-changer for building a robust RAG system. It’s not just about slapping a filename on a chunk; it's about creating a rich, queryable index for your data that unlocks advanced filtering.
Here are three powerful enrichment strategies to improve retrieval:
-
Generating Summaries: Use an LLM to generate a concise summary for each chunk. This distilled meaning can be embedded alongside the original text, often improving retrieval for broader queries.
-
Keyword and Entity Extraction: Apply Named Entity Recognition (NER) to automatically extract and tag key entities like people, organizations, dates, or product names. This creates structured tags for filtering. Learn more about how Named Entity Recognition works in NLP.
-
Applying Custom Schemas: This is where you tailor the system to your specific domain. Define a structured JSON schema with typed fields like
department: "legal",status: "final_draft", orsecurity_clearance: "level_3". This allows for incredibly granular filtering that mirrors your organization's internal logic.
Building A Robust Filtering Mechanism
With these enrichment layers in place, you can build a filtering mechanism that gives users surgical control. This is critical in enterprise settings where documents have complex lifecycles and access permissions.
Imagine a knowledge base for a large corporation. An analyst needs to find information on a project, but only from documents created by the finance department in the last six months marked as "final." Without metadata, this is nearly impossible.
With a rich metadata schema, the retrieval logic becomes a simple two-step process:
- Filter: Select chunks where
department == "finance"ANDcreated_date > six_months_agoANDstatus == "final". - Search: Run the vector search for the user's query only within this pre-filtered subset.
This guarantees that every result is not just semantically related but also meets all explicit criteria. This is how you build a truly reliable and trustworthy RAG system—by transforming a document archive into a precise, queryable database.
Integrating Your Processed Data Into RAG Pipelines
Your documents are cleaned, chunked, and enriched. This high-quality data is the fuel for your RAG system. The final step is to build the bridge between this prepared data and the Large Language Model (LLM) that will generate answers. This is where your automation document processing efforts directly impact the quality of the final output.
This integration is what turns a static collection of processed text into a dynamic, searchable knowledge base that actively assists the LLM.
<iframe width="100%" style="aspect-ratio: 16 / 9;" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/sVcwVQRHIc8" frameborder="0" allow="autoplay; encrypted-media" allowfullscreen></iframe>Exporting to Your Vector Database
First, you must load your prepared chunks and their metadata into a vector database. Whether you're using Pinecone, Weaviate, or Chroma, the data package for each chunk is standardized.
For every chunk, you must export:
- The Content: The raw text of the chunk.
- The Vector Embedding: The numerical representation of the chunk's meaning.
- The Metadata: A structured object (usually JSON) containing all enrichments—summaries, keywords, source information, and custom tags.
This three-part structure is essential. The vector powers the semantic search, but the metadata enables the precision filtering that is critical for high-quality retrieval.
Understanding The RAG Architectural Pattern
At its core, the RAG architecture is a simple and powerful loop designed to ground an LLM in factual context before it generates a response. This prevents the model from relying on its generalized (and often outdated) training data.
Here’s the process when a user asks a question:
- Query Vectorization: The user’s question is converted into a vector embedding using the same model that processed your documents.
- Hybrid Retrieval: This is a two-step search designed for maximum relevance. First, the system applies metadata filters to narrow down the dataset. Then, it performs a vector search on that reduced set to find the chunks most semantically similar to the user's query.
- Context Injection: The top-ranked chunks are retrieved, and their text is inserted into the prompt sent to the LLM. This prompt is structured to instruct the LLM to base its answer solely on the provided information, a practice known as prompt engineering.
The retrieval-first approach is the essence of RAG. You aren't asking the LLM what it knows; you are providing it with the facts and asking it to synthesize an answer.
Tackling Common Integration Challenges
Connecting these components can present challenges that directly affect retrieval quality. Being aware of them is the first step to building a robust system.
A primary challenge is managing the context window. LLMs have a finite limit on the amount of text they can process in a single prompt. If your retrieval step returns too much text (either too many chunks or oversized chunks), you will exceed this limit. Actionable insight: Tune your retrieval logic to return a balanced number of chunks (e.g., top 3-5) and ensure your chunking strategy produces reasonably sized chunks to avoid this issue.
Another critical component is maintaining source traceability. For users to trust the system, they must be able to verify the source of the information. Actionable insight: Ensure the metadata for every chunk includes a precise reference to its origin (e.g., document name, page number) and display this information alongside the generated answer. This traceability turns a black-box AI into a transparent and trustworthy tool.
Evaluating Performance And Overcoming Real-World Hurdles
Deploying a pipeline for automated document processing is just the beginning. The true measure of success is its performance in a real-world environment. Your focus must shift from just building the pipeline to rigorously evaluating and operationalizing it to ensure it is trustworthy and reliable.
For RAG systems, evaluation is nuanced. You must answer two key questions: Did the system retrieve the correct information, and did the LLM use that information faithfully to construct its answer?
Key RAG Performance Metrics
To get an accurate picture of your pipeline's effectiveness, you must track metrics that diagnose the performance of both the retrieval and generation components.
- Context Precision: Measures the relevance of the retrieved chunks. A high score means your retriever is finding signal, not noise.
- Context Recall: Measures whether all the necessary information to answer the query was retrieved. Low recall is a common cause of incomplete answers.
- Faithfulness: Measures whether the LLM's generated answer is factually consistent with the provided context. Low faithfulness indicates the model is hallucinating or ignoring its instructions.
Actionable insight: Regularly evaluating these three metrics provides a complete health check of your RAG system. It tells you whether a problem lies with your retrieval strategy (low precision/recall) or the generation model (low faithfulness), allowing you to focus your optimization efforts where they will have the most impact.
Addressing Critical Operational Concerns
When moving to production, data privacy and operational security become paramount. For documents containing sensitive information—financial data, PII, or proprietary IP—using third-party APIs is often a non-starter due to compliance and security risks.
This is where self-hosting your pipeline is the most actionable solution. By keeping the entire workflow within your own infrastructure, you maintain complete control over your data. For any organization in a regulated industry, this is non-negotiable.
Fortunately, you don't have to build everything from scratch. Open-source, Docker-based tools like ChunkForge provide a clear path to self-hosting. This enables you to leverage powerful processing and chunking capabilities while ensuring full data sovereignty. You get the best of both worlds: advanced features and ironclad security, equipping you to build a system that’s not just powerful, but also production-ready.
Your Top Questions, Answered
Here are practical answers to common questions that arise when automating document processing for RAG systems, with a focus on actionable insights for improving retrieval.
What's The Biggest Mistake People Make In RAG Document Processing?
The single biggest mistake is hyper-focusing on the LLM while neglecting the quality of the retrieval pipeline. Teams spend weeks fine-tuning models but feed them data processed with a naive chunking strategy and no metadata enrichment.
If your chunks are contextually fragmented and you lack metadata for precision filtering, your retrieval will be poor. This leads to irrelevant context being fed to the LLM, resulting in low-quality answers.
Actionable Insight: Treat your data processing pipeline with the same importance as your LLM. Garbage in, garbage out. The quality of your retrieval directly limits the quality of your entire RAG system.
How Do I Choose Between Paragraph And Semantic Chunking?
Your choice should be driven by your document structure and the goal of preserving context for retrieval.
-
Paragraph or heading-based chunking is the best starting point for structured documents like technical manuals, legal contracts, or reports, where formatting already delineates ideas.
-
Semantic chunking is superior for dense, unstructured text where ideas flow across paragraph breaks. It is better at identifying thematic boundaries, creating more coherent chunks for retrieval.
Actionable insight: Don't guess. Run a representative sample of your documents through both methods. Visually inspect the resulting chunks to determine which strategy produces more coherent, self-contained units of information for your specific content.
Should I Use A Cloud Service Or Self-Host This Pipeline?
This decision hinges almost entirely on security, compliance, and data control.
If you handle sensitive data (customer info, financial records, health records) subject to regulations like GDPR or HIPAA, self-hosting is the most secure and compliant option. It ensures your data never leaves your infrastructure.
Cloud services offer convenience but introduce third-party risk. A pragmatic middle ground is to use open-source, containerized tools. They provide powerful, easy-to-deploy features that you can manage on your own servers, giving you both capability and control.
Ready to get your document processing workflow right? With ChunkForge, you can visually inspect your chunks, fine-tune your strategies, and enrich your data to build rock-solid RAG systems in a fraction of the time.
Start your free trial today and see what your documents are really made of.