Unlocking RAG Precision with a Knowledge Graph
Discover how to revolutionize your RAG systems using a knowledge graph. Learn to build and integrate structured data for smarter, more accurate AI responses.
A knowledge graph is a structured, interconnected map of your data that represents real-world things (entities) and the relationships between them. For a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system, it's the key to moving beyond simple text search to achieve deep contextual understanding and factual accuracy. By integrating a knowledge graph, you provide the RAG pipeline with a verifiable source of truth, enabling it to retrieve and generate answers with far greater precision.

Beyond Vectors: Why RAG Needs a Knowledge Graph
Standard Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) relies on vector search, which is excellent at finding semantically similar information. However, this approach has a critical blind spot: it lacks a deep understanding of explicit relationships and facts. This is a primary cause of LLM "hallucinations"—responses that sound plausible but are factually incorrect.
Vector search might know that documents mention "Apple Inc." and "Tim Cook," but it doesn't explicitly understand the connection. A knowledge graph solves this by storing a structured fact: Tim Cook (person) IS_CEO_OF Apple Inc. (organization). This gives the RAG system a ground truth to anchor its retrieval process.
Actionable Insight: Use a Knowledge Graph for Factual Grounding
The most immediate benefit of a knowledge graph in a RAG system is its ability to perform exact matching on facts. While vector search handles fuzzy, conceptual queries, a knowledge graph provides the hard, verifiable connections needed for high-stakes domains.
By integrating a knowledge graph, you can enable your RAG system to:
- Verify Relationships Before Generation: Query the graph first to pull factual context (e.g., confirming a person's job title or a company's acquisition date) and inject it into the prompt. This dramatically reduces hallucinations.
- Answer Multi-Hop Questions: Resolve complex queries like, "What products are made by the company that acquired Fusion Systems?" by traversing the graph's relationships—a task impossible for vector search alone.
- Increase Transparency: Trace an answer directly back to the specific entities and relationships in the graph, making the AI's reasoning transparent and auditable.
The goal is to enrich the retrieval context before the LLM generates a response. By querying the knowledge graph first, the RAG pipeline builds a foundation of factual context, leading to more accurate and trustworthy answers.
If you're new to the core concepts, our detailed guide on Retrieval Augmented Generation offers a great starting point for understanding the foundational architecture.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Knowledge Graph
To effectively use a knowledge graph to improve RAG retrieval, you need to understand its core components. This structure is what provides the precise, factual context that vector search alone cannot deliver.

This structured way of organizing data is why the knowledge graph market is taking off. Valued at USD 1.06 billion in 2024, it’s expected to rocket to USD 6.93 billion by 2030. That’s a staggering 36.6% CAGR, all driven by the need for smarter AI that can cut through complex data with real accuracy. You can read more about the factors behind this explosive market growth.
Entities: The Nouns of Your Data
Entities are the individual nodes in your graph—the specific people, products, locations, or concepts you want your RAG system to know about. For example, in a financial RAG system, entities could be "Tesla, Inc.," "Elon Musk," or "Gigafactory Texas."
Actionable Insight: Define entities that represent the key subjects your users will ask about. This allows your RAG system to retrieve specific, unambiguous facts instead of just finding documents where a name happens to appear.
Relationships: The Verbs That Connect Everything
Relationships are the directed edges that connect entities, defining how they interact. They create a web of context that allows the RAG system to reason its way from one fact to another. For example: (Elon Musk, IS_CEO_OF, Tesla, Inc.) and (Tesla, Inc., OPERATES, Gigafactory Texas).
These connections form triples (subject-predicate-object), the fundamental building block of the graph.
Actionable Insight: Define relationships that capture the most important interactions in your domain. This enables the RAG system to follow these paths to answer complex, multi-part questions that standard retrieval methods would fail.
Schemas: The Grammar Rules for Your Graph
A schema (or ontology) is the blueprint that defines what types of entities and relationships can exist and how they can connect. It ensures data consistency and prevents nonsensical connections. For example, a schema can enforce a rule that only a "Person" entity can have an IS_CEO_OF relationship with an "Organization" entity.
Actionable Insight: Implement a strict schema to maintain data quality. A reliable schema ensures the graph is a trustworthy source of truth for your RAG system, preventing the retrieval of illogical or incorrect information that could lead to flawed outputs.
How to Build a Knowledge Graph from Raw Documents
Transforming unstructured documents into a queryable knowledge graph is a systematic process that uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to extract structured facts, or triples. This is the foundational work required to supercharge your RAG system's retrieval capabilities.

This isn't just a niche tech trend. In 2024, the global knowledge management market was valued at around USD 773.6 billion and is projected to hit over USD 3.5 trillion by 2034. Graph technologies are a massive part of that growth, with Gartner predicting they will be a core component of 80% of data and analytics innovations by 2025. Clearly, turning messy data into structured knowledge is a huge deal. You can read more about the rise of data-driven decision-making.
Let's break down the actionable steps.
Step 1: Identify Key Entities with NER
The first step is to find the "nouns" in your documents using Named Entity Recognition (NER). This NLP technique automatically identifies and classifies entities like people, organizations, and locations within the text.
From the sentence: "Apex Innovations announced that Dr. Evelyn Reed will lead the new Quantum Division in Berlin."
An NER model identifies:
- Apex Innovations (Organization)
- Dr. Evelyn Reed (Person)
- Quantum Division (Organization/Department)
- Berlin (Location)
Actionable Insight: Configure your NER model to recognize the specific entity types defined in your schema. This ensures that the extracted entities align with your graph's structure, making the data clean and ready for ingestion. This is a critical step in any modern Intelligent Document Processing pipeline.
Step 2: Find Connections with Relation Extraction
Once entities are identified, Relation Extraction finds the "verbs" that link them. This process analyzes the context around entities to determine their relationships.
From our example, a relation extraction model establishes links like:
- The relationship between Dr. Evelyn Reed and Quantum Division is "leads."
- The relationship between Quantum Division and Berlin is "is located in."
Actionable Insight: Train or fine-tune a relation extraction model to recognize the specific relationship types from your schema. This is crucial for converting ambiguous sentences into the precise, structured connections your RAG system needs to answer complex questions accurately.
Step 3: Constructing the Triples
The final step is to combine the entities and relationships into structured triples in the format (Subject-Predicate-Object).
From our sentence, we generate these machine-readable facts:
(Dr. Evelyn Reed, leads, Quantum Division)(Quantum Division, located_in, Berlin)
Actionable Insight: Automate the triple extraction and ingestion process into your graph database. By creating a repeatable pipeline that processes new documents, you build a dynamic, queryable asset that continuously feeds your RAG system with up-to-date, fact-based context, significantly boosting the accuracy and reliability of its answers.
Combining Graph and Vector Search for Hybrid Retrieval
Relying solely on vector search for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is insufficient for fact-intensive applications. The most effective approach is a hybrid retrieval model that combines the semantic search capabilities of vectors with the factual precision of a knowledge graph. This synergy creates a RAG system that is both contextually aware and factually grounded.
Actionable Insight: Implement a Two-Stage Retrieval Process
The core strategy for hybrid retrieval is to use the knowledge graph as a pre-retrieval fact-checker and context builder. Instead of sending a user's query directly to a vector database, the RAG system should first query the knowledge graph to extract relevant, verified facts.
Consider the query: "What products does the company that acquired Fusion Systems in 2023 manufacture?"
A hybrid retrieval workflow would execute as follows:
- Graph Query First: The system first queries the knowledge graph to resolve the factual parts of the question. It finds the company that
(acquired, Fusion Systems)with a(date, 2023)property. - Enrich the Prompt: The verified facts from the graph (e.g., "MegaCorp acquired Fusion Systems in 2023") are used to enrich the original query.
- Perform Vector Search: This enriched, factually-grounded query is then used for a vector search. The search is now more focused, retrieving text chunks that are not only semantically relevant but also consistent with the established facts.
- Generate the Answer: The LLM receives the enriched prompt and the retrieved text, enabling it to generate an answer that is both contextually relevant and factually accurate.
The real power of a knowledge graph in RAG is its ability to perform exact matching. Vector search is a master of finding fuzzy semantic similarities, but a graph delivers the cold, hard facts you need for domains like compliance, legal, or technical support, where precision is everything.
The Hybrid Retrieval Workflow in Action
This two-stage process significantly improves the quality of the final response by filtering out irrelevant or incorrect information at the start. The LLM reasons from a foundation of verified data, not just semantic similarity.
Here’s the actionable workflow to implement:
- Initial Query: A user asks a question.
- Knowledge Graph Query: Translate the natural language question into a formal graph query (e.g., Cypher for Neo4j) to extract relevant entities and relationships.
- Context Enrichment: Use the factual triples returned from the graph to create a new, context-rich prompt.
- Vector Search: Use this new prompt to perform a more targeted vector search. For a deep dive on how to create these chunks effectively, check out our guide on understanding semantic chunking.
- LLM Generation: Send the enriched prompt and retrieved chunks to the LLM for final answer generation.
Comparing RAG Retrieval Methods
This table highlights why the hybrid model is superior for applications requiring high accuracy.
| Feature | Vector Search Only | Knowledge Graph Only | Hybrid Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Prone to plausible-sounding hallucinations when context is ambiguous. | High factual accuracy but limited to explicitly defined relationships. | High factual accuracy grounded by the graph, with broad contextual relevance from vectors. |
| Flexibility | Excellent for open-ended, exploratory queries and discovering concepts. | Best for specific, structured questions with known entities. | Combines the flexibility of semantic search with the precision of structured queries. |
| Explainability | Hard to trace why a specific chunk was retrieved (a "black box"). | Highly explainable; answers can be traced directly to nodes and edges. | Offers strong explainability by showing the factual graph data used to guide retrieval. |
| Complexity | Relatively straightforward to set up and maintain a vector index. | Requires significant upfront effort in data modeling and ingestion. | More complex to implement but delivers significantly higher-quality, trustworthy responses. |
By fusing these two methods, hybrid retrieval creates a RAG system that is far more resilient to factual errors. The knowledge graph acts as an intelligent filter, making sure the context fed to the LLM is not just relevant but also verifiably correct. This is how you get AI-generated answers you can actually trust.
Maintaining and Evaluating Your Knowledge Graph
<iframe width="100%" style="aspect-ratio: 16 / 9;" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/Aw7iQjKAX2k" frameborder="0" allow="autoplay; encrypted-media" allowfullscreen></iframe>A knowledge graph is not a static asset; it's a dynamic system whose value to your RAG pipeline depends on its ongoing quality. Without a strategy for maintenance and evaluation, the graph's data will become outdated, leading to inaccurate retrieval and unreliable AI-generated answers.
Actionable Insight: Establish Quality Metrics and a Feedback Loop
To ensure your knowledge graph remains a trustworthy source of truth for RAG retrieval, you must continuously monitor its quality. Implement automated checks and human-in-the-loop validation focused on three key metrics:
- Completeness: How well does the graph cover the key entities and relationships in your domain? Track the density of connections to identify gaps in knowledge.
- Correctness: Are the facts in the graph accurate? Use automated validation rules (based on your schema) and periodic human review to verify the stored triples.
- Coherence: Does the graph adhere to its schema? Run regular queries to detect and correct illogical connections that could mislead the retrieval process.
By systematically tracking these quality dimensions, you move from hoping your RAG system is accurate to engineering it for reliability. This disciplined approach is essential for building trust in your AI's outputs.
Measuring the Impact on RAG Performance
The ultimate measure of your knowledge graph's success is its tangible impact on your RAG system's output. You must connect graph quality to improvements in retrieval and generation performance.
This process visualizes how a query flows through a hybrid system—first hitting the structured graph, then the semantic vector search, to produce a final, fact-checked answer.
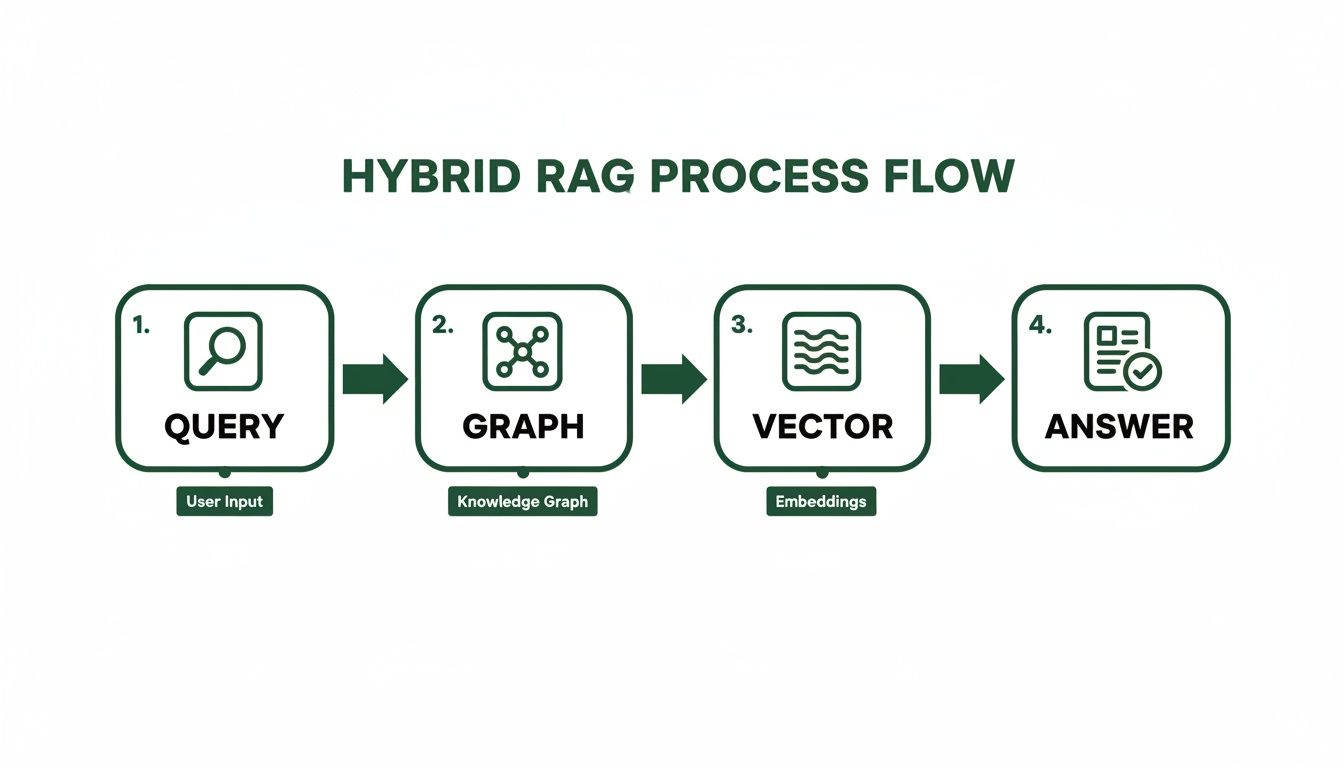
Actionable Insight: Set up an evaluation framework (like RAGAs or A/B testing) to quantify the impact of the knowledge graph on key RAG metrics:
- Retrieval Precision: Measure whether the context retrieved using the graph is more relevant to the user's query compared to vector search alone.
- Answer Faithfulness: Evaluate how well the final answer is supported by the retrieved context. A good graph should increase faithfulness.
- Reduction in Hallucinations: Track the rate of factually incorrect statements with and without the knowledge graph. This is the most critical KPI for demonstrating the graph's value.
The growing investment in this space reflects its critical role. In 2024, the knowledge graph market was valued between USD 1.08 to 1.18 billion. Forecasts project it to reach USD 6.9 billion to 8.9 billion by the early 2030s. This growth highlights the increasing demand for structured, reliable data to power sophisticated AI systems. You can explore more data on the knowledge graph market's future.
Common Questions About Knowledge Graphs in RAG
Implementing a knowledge graph into a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system raises practical questions. Here are actionable answers to the most common challenges teams face.
Why Use a Knowledge Graph Instead of Just Vector Search?
Use a knowledge graph for factual precision and explicit context where vector search alone is insufficient. Vector search excels at finding semantically similar content but cannot verify facts, which leads to hallucinations.
A knowledge graph provides a structured source of truth, offering three key advantages for RAG retrieval:
- Factual Grounding: It allows the RAG system to verify facts before generation, drastically reducing factual errors.
- Complex Query Resolution: It can answer multi-hop questions (e.g., "Who is the CEO of the company that manufactures the part supplied by Vendor X?") by traversing defined relationships.
- Explainability: You can trace an answer back to the specific nodes and edges used, making the AI’s reasoning transparent and auditable.
Actionable Insight: Use vector search for broad, conceptual queries and a knowledge graph for queries that depend on specific, verifiable relationships. The best RAG systems use a hybrid approach, leveraging the graph for facts and vectors for semantic context.
What Use Cases Are Best Suited for a Graph-Enhanced RAG System?
A graph-enhanced RAG system is most valuable in high-stakes domains where factual accuracy is non-negotiable. Prioritize this approach for use cases like:
- Complex Question Answering: In scientific research, financial analysis, or legal discovery, where answers depend on navigating a web of intricate relationships.
- Enterprise Search and Knowledge Management: To create an organizational map that connects employees, projects, and documents, enabling precise information discovery.
- Cybersecurity and Threat Intelligence: To connect disparate security events, threat actors, and internal assets to uncover complex attack patterns.
- Compliance and Regulatory Reporting: To ensure AI-generated reports are built on consistent, verifiable, and correctly interpreted data.
Actionable Insight: If the cost of a factually incorrect answer is high in your application, the upfront investment in building a knowledge graph is justified. It provides the reliability that standard RAG systems lack.
How Do I Get Started Building a Knowledge Graph for RAG?
Start with a focused, manageable scope and expand over time. Follow these four actionable steps:
1. Define Your Schema (Ontology) First, identify the core entities (nouns like Products, Companies) and relationships (verbs like manufactures, acquires) critical to your use case. A simple, well-defined schema is the blueprint for a successful graph.
2. Choose Your Tools Select a graph database to store and query your data. Top choices include:
- Neo4j: A popular native graph database with an intuitive query language (Cypher), ideal for most applications.
- Amazon Neptune: A fully managed AWS service, great for teams already in the AWS ecosystem.
- TigerGraph: A high-performance option designed for massive datasets and real-time queries.
3. Extract Triples from Your Documents
Use NLP models to automate the extraction of (subject, predicate, object) triples from your unstructured text. This involves using Named Entity Recognition (NER) to find entities and Relation Extraction to identify the connections between them. This populates your graph with structured facts.
4. Integrate with Your RAG Pipeline Modify your retrieval workflow to query the knowledge graph first. Use the factual context returned by the graph to enrich the user's prompt before performing a vector search. This two-stage retrieval process is the key to unlocking the accuracy benefits of a hybrid RAG system.
Building production-ready AI systems starts with high-quality data preparation. At ChunkForge, we simplify the most critical step—transforming your raw documents into structured, RAG-ready assets. With advanced chunking strategies, deep metadata enrichment, and a visual interface to verify context, you can build more accurate and reliable retrieval pipelines faster. Get started with our free trial or self-host our open-source solution to maintain full control over your data.