What Is a Tabular Format and Why It Powers Modern AI
Learn what is a tabular format and discover why this simple structure of rows and columns is the key to building high-performance RAG systems and AI pipelines.
At its core, a tabular format is simply information organized into a grid of rows and columns. It's the universal language for structured data, turning raw information into a queryable asset. For Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems, this structure is the key to moving beyond simple semantic search to achieve precise, context-aware, and trustworthy information retrieval.
What Is a Tabular Format in AI?

Imagine a vector database filled with millions of text chunks. Finding relevant information is like searching a library where all the books are piled on the floor. Now, picture that same library, but every book is neatly arranged on shelves (rows) with metadata labels for genre, author, and publication date (columns). That’s the power a tabular format brings to Retrieval-Augmented Generation.
This structure transforms chaotic, unstructured text into a clean, searchable asset. For a RAG system, this organization is essential. RAG models need to find precise, relevant information to generate accurate answers, and a tabular format provides the structured metadata needed to filter and locate that information in a split second, before vector search even begins.
The Foundation of Modern Data Retrieval
In any modern data workflow, information laid out in rows and columns is the bedrock. It’s the foundation for everything from massive relational databases to the simple CSV files you export every day. This structure allows RAG systems to execute complex, multi-faceted queries far beyond basic keyword or vector searches.
For RAG and other LLM-based systems, a tabular format acts as the critical bridge between unstructured documents and the machine-readable data that AI thrives on. When you break a document into smaller pieces—a process you can explore in our guide to data parsing—each chunk can be tracked and managed as its own row in a table.
A key insight for RAG engineers is that tabular metadata turns every text chunk into a queryable object. Instead of just searching for what is in the text, you can filter by when it was created, who wrote it, and what type of information it contains.
This structured metadata, neatly stored in columns alongside the text chunk, unlocks powerful pre-filtering capabilities. For instance, you can use familiar database-style operations to zero in on specific chunks before they are sent to a vector search index. This pre-filtering is a fundamental and actionable technique for boosting the accuracy and efficiency of any RAG system.
How AI Interprets the Anatomy of a Table
To an AI, a table isn't just a grid of data—it's a set of precise instructions. Each component of its anatomy provides the critical context a machine needs to understand relationships and enable powerful, targeted retrieval for systems like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).

Think of it like this: a machine reads a table not as a single image, but by systematically deconstructing its parts. This is how it translates the visual structure we see into logical operations it can actually execute to improve retrieval.
The Core Components of Tabular Data
The fundamental building blocks of any table are its rows, columns, headers, and cells. Each one serves a distinct purpose for enabling advanced retrieval in a RAG pipeline.
-
Columns: From a machine's perspective, columns are metadata fields. A column header like 'Author' defines a filterable attribute for every single entry. This consistency is absolutely vital for implementing precise pre-retrieval filtering.
-
Rows: Each row represents a single data record—such as a document chunk—and connects all its metadata. It links the 'Author' to a specific 'Title', 'Publication Date', and 'Source URL', creating a single, cohesive object for retrieval.
-
Cells: A cell is the single, atomic value at the intersection of a row and a column. It's the specific value, like "Jane Doe," that populates the metadata field for that chunk.
-
Headers: These are the labels at the top of each column, and for an AI, they are the most important part. Headers define the schema—the blueprint for the entire dataset—dictating what each piece of information actually means and enabling consistent querying.
Actionable Insight: Define a rich schema for your document chunks. Include columns for
creation_date,author,department,document_type, andsecurity_level. This schema becomes the foundation for building powerful and secure RAG filtering logic.
Turning Documents into Filterable Assets
This structured anatomy is precisely why a tabular format is so powerful for enriching unstructured documents. When a tool like ChunkForge processes a PDF, it breaks the raw text into smaller "chunks." By themselves, these chunks are just isolated blocks of text.
But by creating a table to manage them, we can attach structured metadata to each one. Each chunk becomes a row, and we add columns for searchable attributes.
This transforms a simple document into a filterable intelligence asset, ready for advanced retrieval. Each chunk is no longer just text but an entry with specific metadata tags like 'source_document' or 'department'—the exact kind of attributes you need for precise filtering in a RAG pipeline.
Boosting RAG Accuracy with Tabular Metadata
A RAG system running on pure semantic search is often imprecise. If a user asks for "financial reports," a vector search might return every document that mentions money—a firehose of information that often includes irrelevant or outdated content. This is where structured, tabular metadata becomes an engineer's most valuable tool for improving retrieval quality.
By storing key details about each document chunk in a table, you give your RAG system a powerful new tool: metadata filtering. Instead of just asking "what's the most similar content?", you can apply strict rules before the vector search even kicks off. This hybrid approach is the key to unlocking surgical retrieval accuracy.
From Vague Search to Surgical Precision
This shift transforms your retrieval process from a blunt instrument into a surgical tool. You can now implement retrieval strategies that dramatically improve the quality of the context provided to the LLM.
Actionable Retrieval Strategies:
- Time-Based Filtering:
SELECT chunk FROM documents WHERE creation_date > '2024-01-01'before passing the results to a vector search. This ensures the LLM only receives recent, relevant information. - Source-Based Filtering:
SELECT chunk FROM documents WHERE department = 'Finance'to restrict the search to a specific source, improving contextual accuracy. - Access Control:
SELECT chunk FROM documents WHERE access_level = 'confidential'to implement security and compliance rules at the retrieval stage.
This pre-filtering step acts as a gatekeeper, drastically narrowing the search space to only the most relevant candidates. The LLM then receives a much smaller, pre-qualified set of documents, which directly slashes the risk of it generating inaccurate or "hallucinated" responses. Improving your AI document processing pipeline with this metadata-first approach builds a more trustworthy system from the ground up.
Connecting Your Content to Real-World Behavior
The real power of tabular data becomes obvious when you realize just how much of the digital world runs on it. With roughly 5.44 billion internet users generating clickstreams, search queries, and payment logs, almost all of this behavioral data ends up in tables. You can find out more about these trends in global internet usage statistics.
This is where unstructured content and structured data meet. A single PDF might be split into dozens of chunks, but each of those chunks can be tracked as a row in a table. Now you can link that chunk to behavioral data—who viewed it, when they viewed it, and what they did next.
The hybrid approach—filtering with structured metadata first, then performing a semantic search on the smaller, pre-qualified dataset—is how you build truly intelligent and trustworthy RAG systems. It's the secret to ensuring relevance, accuracy, and security.
Ultimately, this strategy lets engineers connect human knowledge (from documents) with user behavior (from logs). What was once a messy, custom engineering task becomes a straightforward database join. Your RAG system can now understand not just what information exists, but how people are actually using it, leading to far more context-aware and useful AI responses.
Unlocking Tables Hidden Within Your Documents
Much of an organization's most valuable structured data isn't in a clean database; it's trapped inside tables within PDFs, reports, and presentations. A common mistake in RAG pipelines is to extract this content as plain text, which destroys the row-and-column structure that gives the data its meaning. This turns a pristine dataset into a jumbled mess of words, rendering it useless for precise retrieval.
Cleanly extracting these embedded tables is a non-negotiable first step for building a high-performance RAG system. The goal is to preserve the table's original architecture. Before an AI can leverage tabular data for retrieval, you have to get it out of the source document intact. You can learn more about how to extract data from PDF files and overcome the common challenges of malformed copy-pastes.
Preserving Structure for Deeper Understanding
Modern extraction tools are designed to understand and preserve the complex structures within documents that would otherwise corrupt your data.
- Merged Cells: Capable tools correctly interpret cells spanning multiple rows or columns, maintaining data relationships.
- Complex Headers: Hierarchical or multi-level headers are preserved, which is crucial for understanding the data's nested logic.
- Implicit Relationships: The position of data is critical metadata. Preserving the original row and column context is essential for answering relational queries.
Losing this structural information makes it impossible for a RAG system to answer complex questions. For a deeper look at the technical process, check out our guide on extracting tables from PDFs specifically for AI workflows.
This is where structured data really shines. It allows for a much more precise filtering process in RAG, letting you narrow down the search before it even hits the vector database.
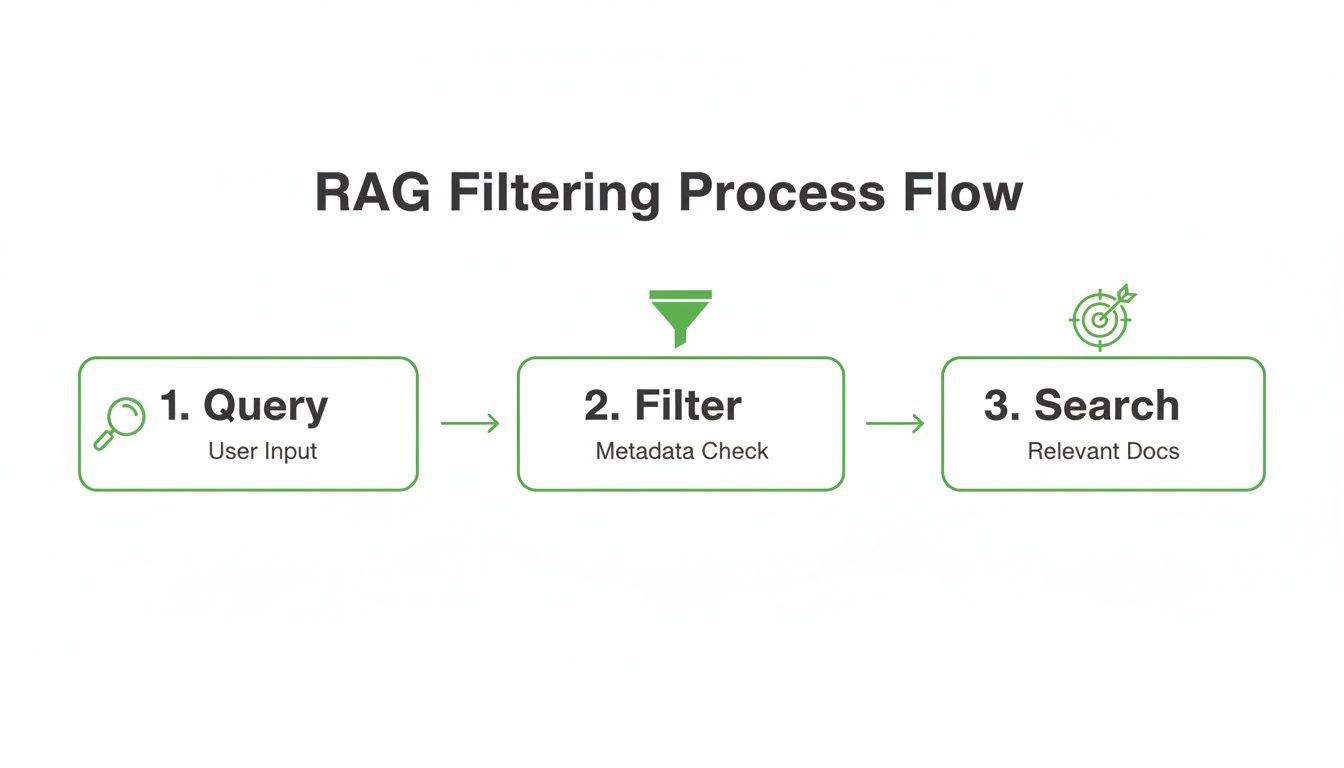
As you can see, filtering with tabular metadata isn't just an extra step—it's a critical middleman that makes sure your final search is running on a highly relevant, pre-qualified set of documents.
Validating Extraction with Visual Tools
Even with the best automated tools, validation is crucial. How can you be certain that the extracted data perfectly mirrors the original? This is where visual mapping becomes essential.
Actionable Insight: By preserving the original table structure as metadata, you empower your RAG system to understand the relationships between data points. This allows it to answer sophisticated questions that would be impossible with flat text alone.
Tools like ChunkForge provide a visual overlay, mapping each extracted cell back to its precise location in the original PDF.
This visual feedback loop allows engineers to instantly spot and correct extraction errors—such as a shifted column or a broken row—long before bad data pollutes the vector database and degrades LLM performance. This verification acts as a final quality check, ensuring the RAG system learns from a perfect digital twin of the source table, not a corrupted copy.
Best Practices for Preparing AI-Ready Tabular Data
<iframe width="100%" style="aspect-ratio: 16 / 9;" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/WpX2F2BS3Qc" frameborder="0" allow="autoplay; encrypted-media" allowfullscreen></iframe>Getting your data into a neat table is only the first step. To optimize a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system for high performance, that data must be clean, consistent, and structured for machine interpretation. A messy table is a silent killer for retrieval accuracy, leading to poor-quality context and difficult-to-trace failures.
The journey often begins by pulling raw information from various sources. If you're looking for a deep dive into that initial step, there are some excellent guides on scraping data specifically for AI applications.
Data preparation is foundational. A systematic checklist ensures your RAG system is built on reliable, high-quality information. This isn't just about fixing typos; it's about structuring data so an AI can leverage it for precise retrieval.
Create a Bulletproof Data Schema
Before ingesting any data, define a strict schema. A schema is the blueprint for your table, specifying column names and their expected data types (e.g., string, integer, datetime).
For a RAG system, enforcing a schema is your first line of defense against data corruption. It guarantees that every row adheres to the same rules, making filtering operations predictable and reliable.
Your RAG system is only as good as the data it retrieves. A rigorous schema and validation process are the quality control gates that protect your AI from learning from corrupted, inconsistent, or nonsensical information.
Handle Missing Values and Inconsistencies
Real-world data is inherently messy. Your tables will have blank cells, inconsistent formats, and other anomalies. Leaving these unaddressed will break your retrieval logic.
Actionable Data Sanitization Checklist:
- Tackle Missing Values: Implement a consistent strategy for nulls. Fill them with a default value like "N/A" for text fields or 0 for numerical ones. This prevents errors in systems that cannot handle null values during filtering.
- Standardize Date and Time Formats: Enforce a single, machine-readable format for all timestamps, such as ISO 8601 (
YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ). This is non-negotiable for reliable time-based filtering. - Normalize Categorical Data: Standardize text fields with synonyms. For instance, "USA," "U.S.A.," and "United States" should all be mapped to a single value to ensure filters like
country = 'USA'work correctly. - Normalize Numerical Data: For columns with wide-ranging numerical values, consider normalizing them to a common scale (e.g., 0 to 1). This can be important for more advanced retrieval models that might use these values as features.
Validate Data Before Ingestion
This is your final, most important step: validate every piece of data before it enters your vector database or RAG pipeline.
Implement automated validation scripts that check each row against your schema. These scripts should verify data types, ensure required fields are not empty, and confirm that values fall within expected ranges (e.g., a "percentage" column should not exceed 100).
This validation step is your last line of defense. By catching errors early, you prevent bad data from poisoning your AI, ensuring your retrieval process remains fast, accurate, and reliable.
Common Questions About Tabular Formats in RAG
When you start pulling structured data into your AI systems, you’re bound to run into a few common questions. It’s just part of the process. Getting straight answers is key to building a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline that actually benefits from the power of tabular data.
Let's walk through the most frequent challenges and clear up the concepts you'll need to solve real-world problems.
How Does Tabular Metadata Actually Improve RAG?
This is a big one. Why go through the trouble of adding metadata when you could just rely on pure vector search? The answer comes down to precision and context.
Vector search is fantastic at finding content that’s semantically similar, but it often misses the specific, hard-and-fast context that business applications demand. Think of tabular metadata as a powerful bouncer at the door of your search club.
For example, before the vector search even kicks off, you can instantly filter your document chunks to only include those created in the last year, authored by the legal team, and marked as 'final'. This small step radically shrinks the search space.
By narrowing the pool of potential documents, you ensure the LLM receives only highly relevant, accurate, and up-to-date information. This hybrid approach—filter first, then search—significantly increases retrieval precision, reduces hallucinations, and enables critical security features like access control.
What are the Biggest Pitfalls in Table Extraction?
Another tricky area is pulling tables out of PDFs and other documents. The most common mistakes are almost always structural.
We see it all the time: failing to identify complex headers that span multiple rows, misinterpreting merged cells (which completely breaks row-column alignment), or accidentally treating footnotes as part of the table data. These errors corrupt the data's structure, rendering it totally useless for any kind of analysis.
This is why using a tool with a visual overlay is so important. It lets you map the extracted data directly back to the source document, so you can spot and fix these structural issues before they poison your entire AI pipeline.
Can You Use Tabular Formats for Non-Text Data?
Absolutely. A tabular format is perfect for managing the metadata tied to any kind of data, not just text. It’s incredibly versatile.
- For Images: Each row could represent a single image, with columns for metadata like resolution, object tags detected by a vision model, or the date it was taken.
- For Audio: A row might correspond to an audio clip, with columns for the transcript, speaker ID, or timestamps of key phrases.
This kind of structured metadata is what makes powerful, multi-modal RAG systems possible. You can filter and retrieve information based on specific attributes of your images or audio files, not just their semantic meaning.
Is CSV Always the Best Storage Format?
Finally, let's talk storage. Is CSV always the best choice? While it's universal and easy to use, it's not always the best tool for the job. Its biggest weakness is the lack of a strict schema, which often leads to annoying data type problems, like numbers getting read as text.
For any serious, large-scale AI pipeline, columnar formats like Parquet or ORC are far more efficient. They offer better compression and much faster query performance because you only have to read the specific columns you need for a given query, not the whole file.
So, while CSV is fine for getting started or for small-scale development, migrating to a more robust format like Parquet is a smart move for production systems that handle millions of chunks.
Turn your unstructured documents into high-quality, retrieval-ready assets with ChunkForge. Our visual document studio makes it easy to extract tables, enrich chunks with structured metadata, and export your data in the perfect format for any RAG pipeline. Start your free trial today and build a smarter AI foundation at https://chunkforge.com.